Student loans are sometimes a necessary evil, but they can also be a great way to invest in your future. If you’re considering taking out a student loan, it’s important to know how much your monthly payments will be so you can plan accordingly.
Payment Amounts and Terms
Student loan payments are based on the amount borrowed, interest rates, and other factors. They are generally divided into fixed payments for 10-15 years (or until the balance is paid off).
The monthly payment amount depends on the type of loan: Federal or private. Federal loans have lower interest rates than private loans but require more paperwork than private loans. Private loans are not guaranteed by the federal government but may offer better terms than federal loans. The interest rate for both types of loans is determined by market conditions at the time of origination.
Federal student loan repayment plans are based on income level; borrowers with higher incomes pay higher monthly payments than those with lower incomes. Private lenders set their own terms including payment amounts and length of repayment periods ranging from five to twenty years depending on how much money you borrow and how long you take to pay it back (up
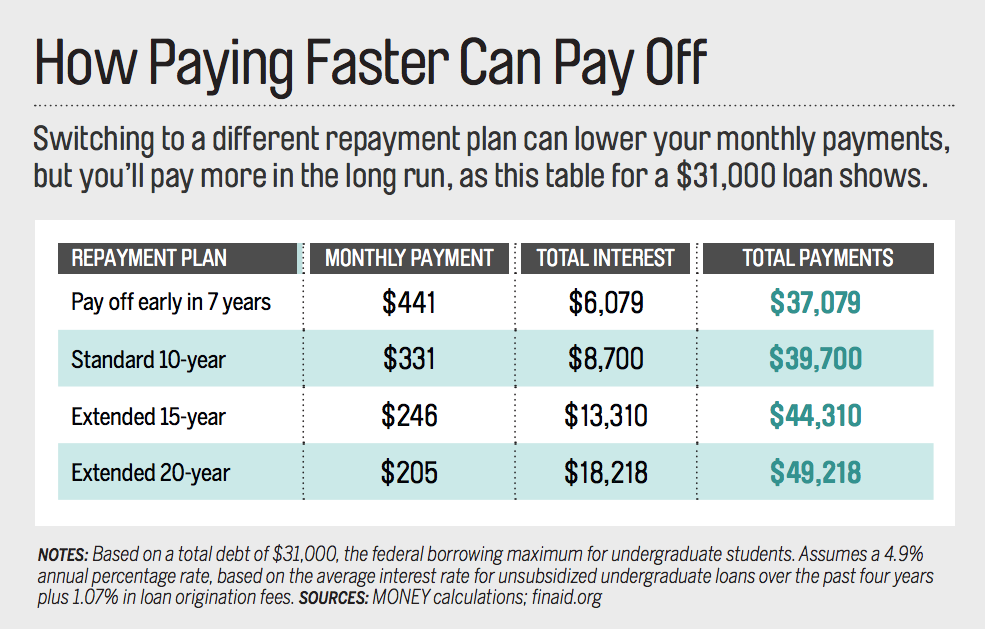
How Much Are Student Loans Payments
The typical monthly student loan payment among borrowers who were actively repaying their loans in 2019 was between $200 and $299, according to the Federal Reserve. But your monthly bill may be much lower or higher than that. Your required payment depends on the amount you initially borrowed, your interest rate and the repayment plan you’ve chosen.
It’s possible to change your payment amount if you want to save money or pay off your loans faster, and there are many ways to estimate how much you’ll pay when you first borrow. Here’s what you need to know.
student loan forgiveness
If you are employed by a U.S. federal, state, local, or tribal government or not-for-profit organization, you might be eligible for the Public Service Loan Forgiveness Program. Keep reading to see whether you might qualify.
To ensure you’re on the right track, you should submit a Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) & Temporary Expanded PSLF (TEPSLF) Certification & Application (PSLF Form) annually or when you change employers. We’ll use the information you provide on the form to let you know if you are making qualifying PSLF payments. This will help you determine if you’re on the right track as early as possible.
*This provision will be waived through October 31, 2022 as part of the limited PSLF waiver. Learn more.
Suspended Payments Count Toward PSLF and TEPSLF During the COVID-19 Administrative Forbearance
If you have a Direct Loan and work full-time for a qualifying employer during the payment suspension (administrative forbearance), then you will receive credit toward PSLF or TEPSLF for the period of suspension as though you made on-time monthly payments in the correct amount while on a qualifying repayment plan.
To see these qualifying payments reflected in your account, you must submit a PSLF form certifying your employment for the same period of time as the suspension. Your count of qualifying payments toward PSLF is officially updated only when you update your employment certifications.
Digital signatures from you or your employer must be hand-drawn (from a signature pad, mouse, finger, or by taking a picture of a signature drawn on a piece of paper that you then scan and embed on the signature line of the PSLF form) to be accepted. Typed signatures, even if made to mimic a hand-drawn signature, or security certificate-based signatures are not accepted.
Note: In-grace, in-school, and certain deferment, forbearance, and bankruptcy statuses are not eligible for credit toward PSLF.
Have questions? Find out what loans qualify and get additional information about student loan flexibilities due to the COVID-19 emergency.
Qualifying Employer
Qualifying employment for the PSLF Program isn’t about the specific job that you do for your employer. Instead, it’s about who your employer is. Employment with the following types of organizations qualifies for PSLF:
- Government organizations at any level (U.S. federal, state, local, or tribal) – this includes the U.S. military
- Not-for-profit organizations that are tax-exempt under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code
Serving as a full-time AmeriCorps or Peace Corps volunteer also counts as qualifying employment for the PSLF Program.
The following types of employers don’t qualify for PSLF:
- Labor unions
- Partisan political organizations
- For-profit organizations, including for-profit government contractors
Contractors: You must be directly employed by a qualifying employer for your employment to count toward PSLF. If you’re employed by an organization that is doing work under a contract with a qualifying employer, it is your employer’s status—not the status of the organization that your employer has a contract with—that determines whether your employment qualifies for PSLF. For example, if you’re employed by a for-profit contractor that is doing work for a qualifying employer, your employment does not count toward PSLF.
Other types of not-for-profit organizations: If you work for a not-for-profit organization that is not tax-exempt under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code, it can still be considered a qualifying employer if it provides certain types of qualifying public services.
Full-time Employment
For PSLF, you’re generally considered to work full-time if you meet your employer’s definition of full-time or work at least 30 hours per week, whichever is greater.
If you are employed in more than one qualifying part-time job at the same time, you will be considered full-time if you work a combined average of at least 30 hours per week with your employers.
If you are employed by a not-for-profit organization, time spent on religious instruction, worship services, or any form of proselytizing as a part of your job responsibilities may be counted toward meeting the full-time employment requirement.
Eligible Loans
Any loan received under the William D. Ford Federal Direct Loan (Direct Loan) Program qualifies for PSLF.
Loans from these federal student loan programs don’t qualify for PSLF: the Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program and the Federal Perkins Loan (Perkins Loan) Program. However, they may become eligible if you consolidate them into a Direct Consolidation Loan.
Student loans from private lenders do not qualify for PSLF.
Under normal PSLF Program rules, if you consolidate your loans, only qualifying payments that you make on the new Direct Consolidation Loan can be counted toward the 120 payments required for PSLF. Any payments you made on the loans before you consolidated them don’t count. However, if you consolidate these loans into a Direct Loan before October 31, 2022, you may be able to receive qualifying credit for payments made on those loans through the limited PSLF waiver.